What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes, also known as K8s, is an open-source container orchestration platform for managing containerized workloads and services, that facilitates both declarative configuration and automation. It has a large, rapidly growing ecosystem. Actually, Google built this platform in 2014. But the Cloud Native Computing Foundation now maintains the project (CNCF). Kubernetes defines a set of building blocks ("primitives") that collectively provide mechanisms that deploy, maintain and scale applications based on CPU, memory, or custom metrics.
It's an open-source giving you the freedom to take advantage of on-premises, hybrid, or public cloud infrastructure, letting you effortlessly move workloads to where it matters to you.
It has some cool features, such as Automated rollouts and rollbacks, Service discovery and load balancing, Storage orchestration, Secret and configuration management, Automatic bin packing, Batch execution, IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack, Horizontal scaling, Self-healing, Designed for extensibility.

Lens
Kubernetes Lens is an effective, open-source IDE for Kubernetes. It provides users the easiest and fastest path to situational awareness in real-time for Kubernetes applications and clusters. With a context-aware terminal, built-in Prometheus stats, and instant, and easy access to logs, Lens is the fastest tool for navigating through all layers in the stack, viewing performance data, and troubleshooting issues.
Designed for those who work with Kubernetes on a daily basis
It's interfaced in such a way, like the Hotbars, Command Palette, etc, It's become so handy on daily basis.
- Immediate Situational Awareness in Context Lens provides users the easiest and fastest path to situational awareness in real-time for Kubernetes applications and clusters. With a context-aware terminal, built-in Prometheus stats, and instant, and easy access to logs, Lens is the fastest tool for navigating through all layers in the stack, viewing performance data, and troubleshooting issues.
- Context-Aware Terminal The built-in terminal includes a version of kubectl that is always API-compatible with your cluster and in the right context by automatically downloading and assigning the correct version in the background. As the user switches from one cluster to another, the terminal maintains the correct kubectl version and context.
- Multi-Cluster Management on Any Cloud Access and work with any number of Kubernetes clusters on any cloud, from a single unified IDE. The clusters may be local (e.g. minikube) or external (e.g., Mirantis Kubernetes Engine (formerly Docker Enterprise/UCP), EKS, AKS, GKE, Rancher, or OpenShift). Clusters may be added simply by importing the kubeconfig with cluster details.
- Multiple Workspaces Workspaces are used to organize any number of clusters into logical groups. They are useful for DevOps and SREs who need to manage multiple (even hundreds of) clusters. A single workspace contains a list of clusters and their full configuration.
- Built-In Prometheus Stats See real-time graphs and resource utilization charts integrated into the dashboard, always in the right context. Lens comes with a built-in and multi-tenant Prometheus setup that respects role-based access control (RBAC) for each user. Users will see visualizations for all the namespaces and resources to which they have access.
- Helm Charts Management Helm is the package manager for Kubernetes: most Kubernetes workloads and services are deployed as Helm charts. Lens IDE comes with built-in Helm charts management allowing quick access to and management of thousands of publicly available Helm charts. Users can browse Helm charts, deploy them with a single click, modify configuration settings (with built-in help), explore installed Helm charts and their revisions, and lifecycle manage Helm deployments with single click upgrades.
Installation
⮞ Open the official Lens website through this link
⮞ Download the file which fits your device
⮞ Install it normally. Just set the location of installation, that's it.
⮞ Lens will then automatically run (after installation finishes).
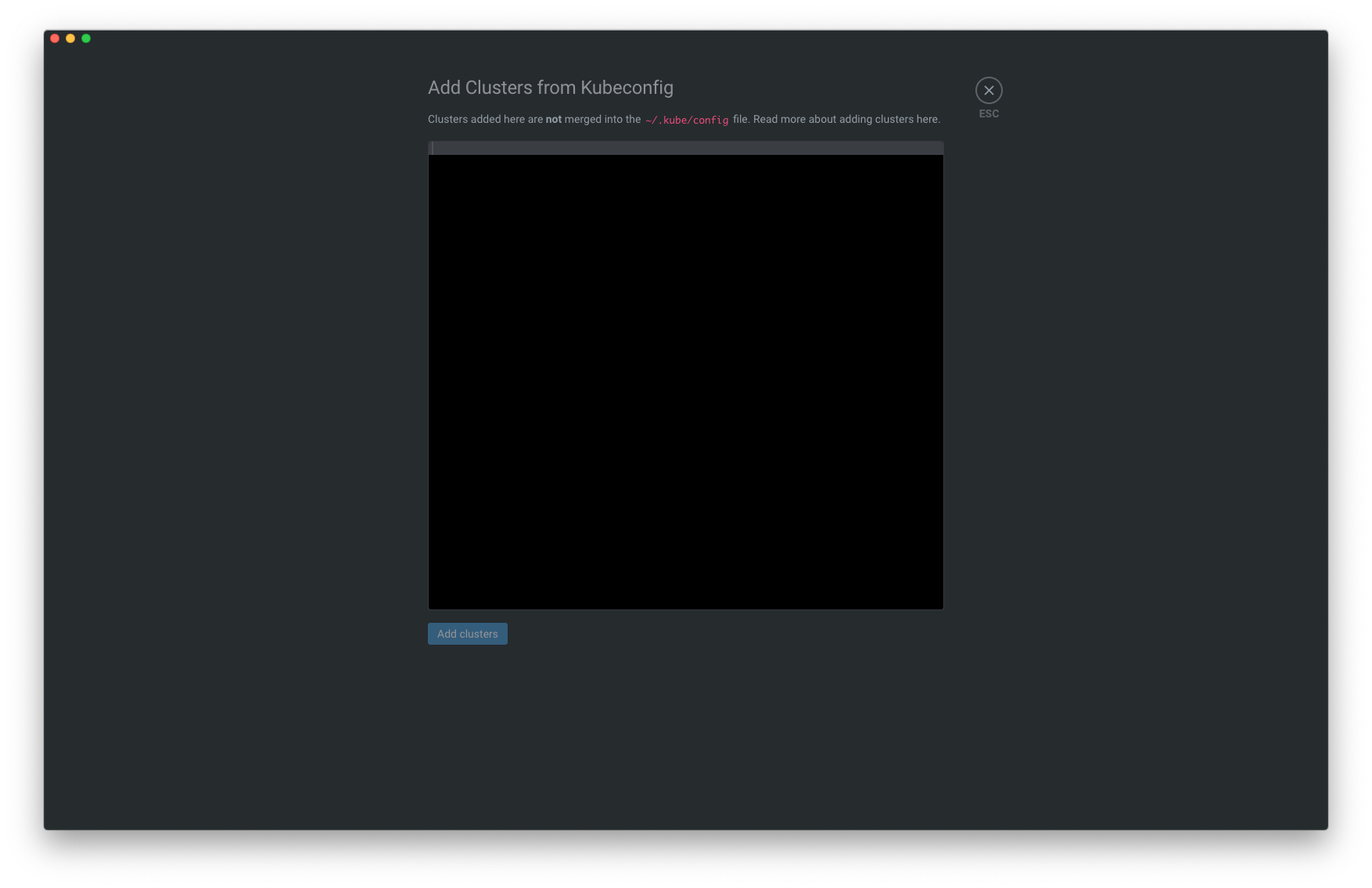
How to create Clusters
To get started with clusters, two things you can do to create a cluster
Click the Add Cluster button (indicated with a '+' icon).
Enter your kubeconfig file directly to the displayed input field.
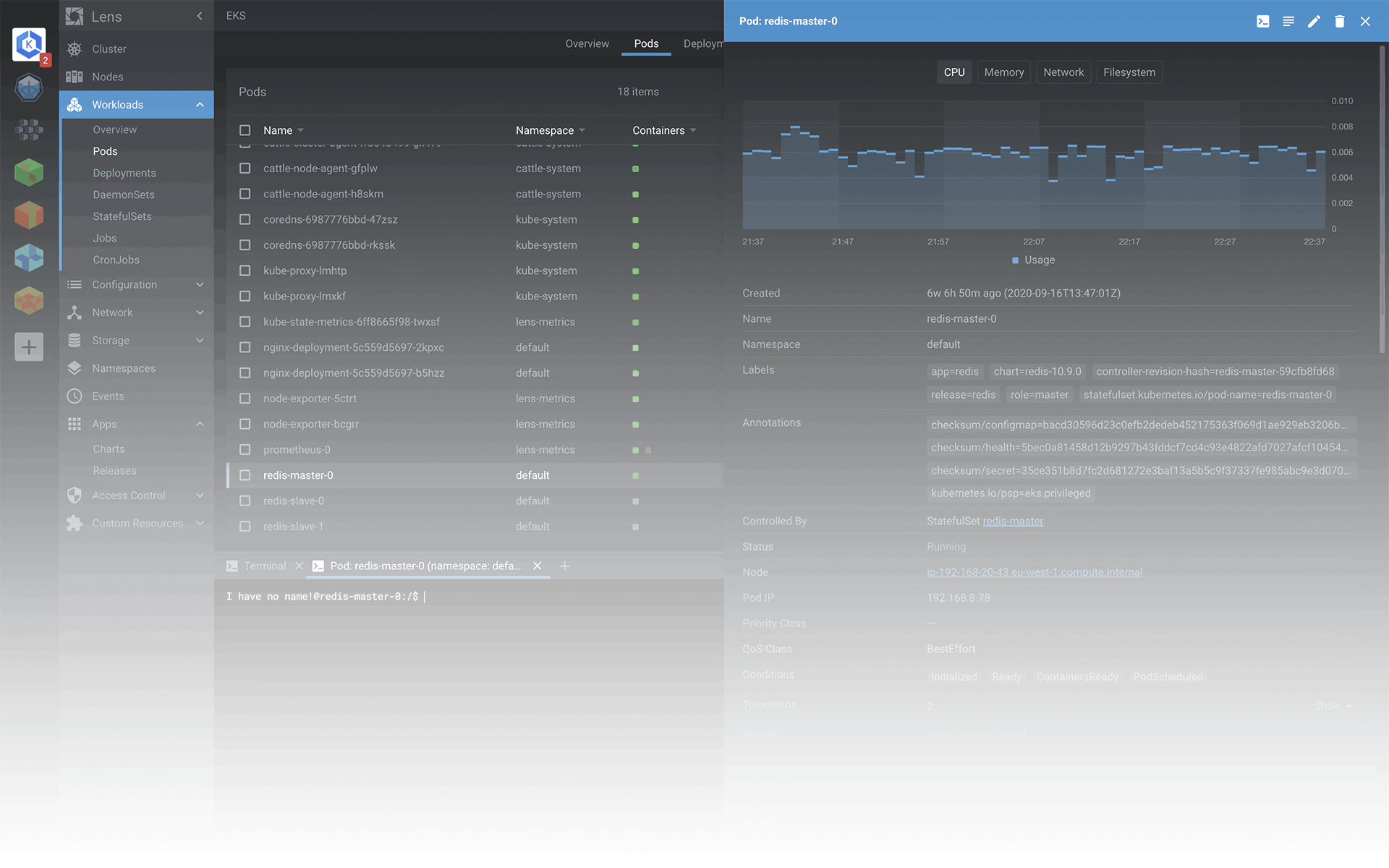
What are Nodes in Lens
A Node is a worker machine in Kubernetes and may be either a virtual or a physical machine, depending on the cluster. A Pod always runs on a Node. You can start by checking if our nodes are up and running in a Ready state. Each Node is managed by the control plane. A Node can have multiple pods, and the Kubernetes control plane automatically handles scheduling the pods across the Nodes in the cluster.
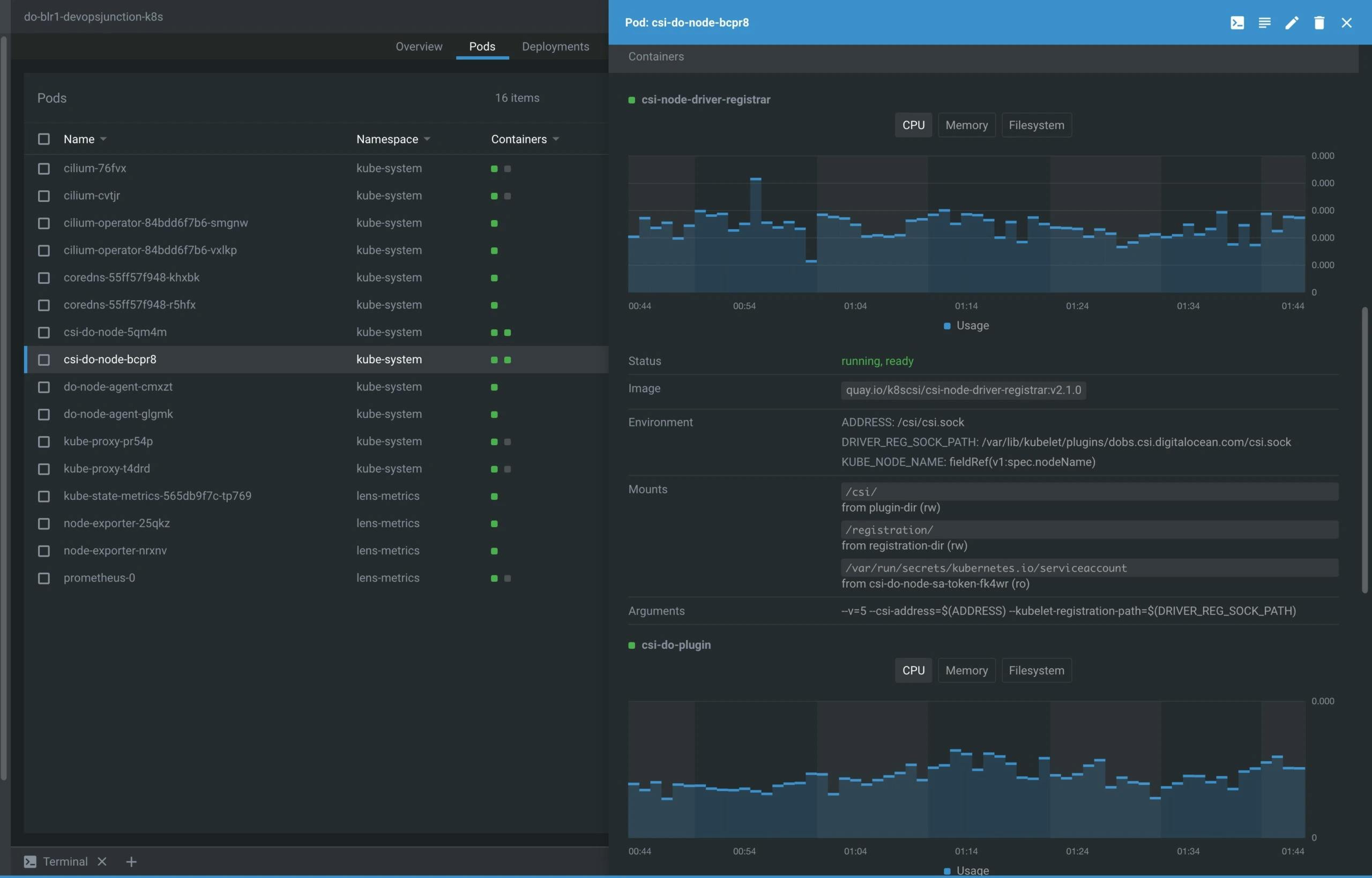
What is Workload in Lens
In this menu, you can see a lot of information about your cluster. It will help you to see the events happening inside your cluster, like how many Pods, Deployments, StatefulSets, DaemonSets, Jobs, and CronJobs are running in it.
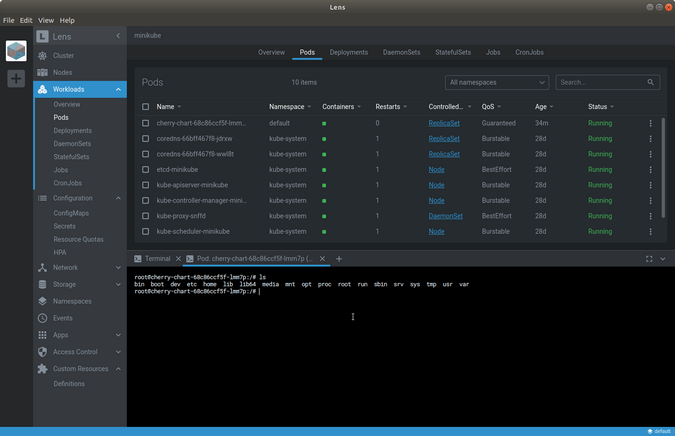
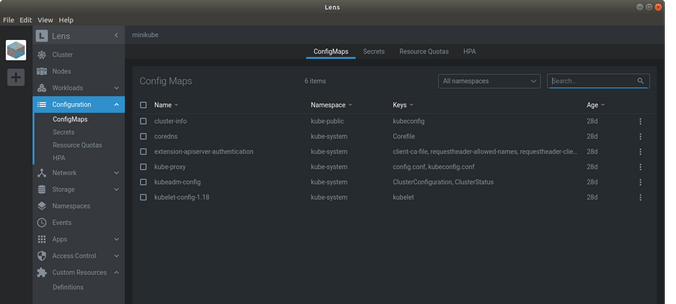
What is Configuration menu in Lens
The configuration shows ConfigMaps, Secrets, Resource Quotas, and Horizontal Pod Autoscalers (HPA).
It's all same, showing you the core details of your cluster like Secrets, which is an object that contains a small amount of sensitive data such as a password, a token, or a key. Such information might otherwise be put in a Pod specification or in a container image. Using a Secret means that you don't need to include confidential data in your application code. So such things you can find in the Configuration menu.
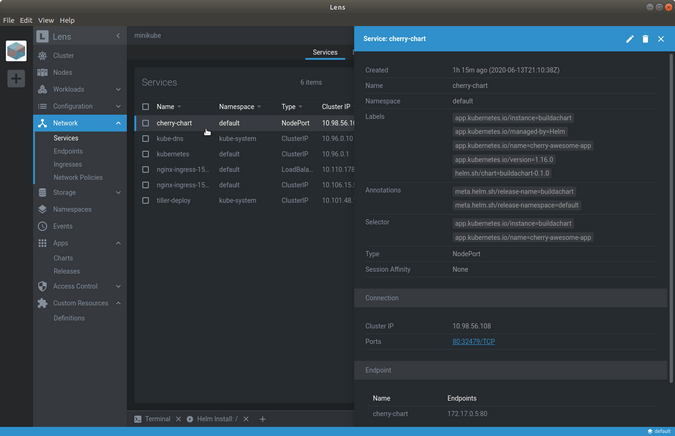
What is Network in Lens
The network includes options for managing your network services, endpoints, ingresses, and network policies.
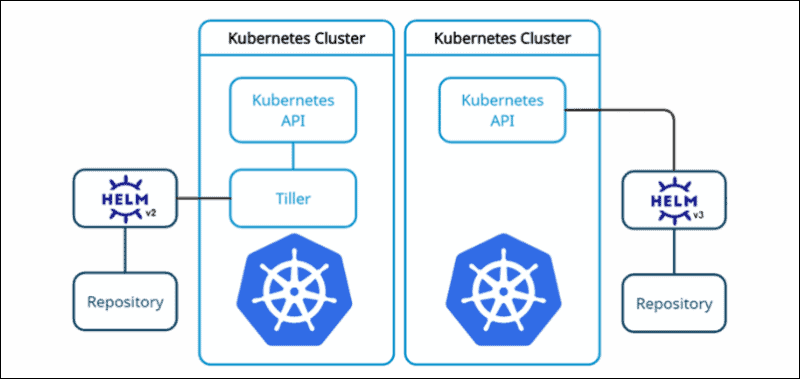
What is Helm in Kubernetes
A small introduction to Helm, it's a Kubernetes deployment tool for automating the creation, packaging, configuration, and deployment of applications and services to Kubernetes clusters.
Helm deploys packaged applications to Kubernetes and structures them into charts. The charts contain all pre-configured application resources along with all the versions into one easily manageable package. It keeps track of the versioned history of every chart installation and change. Rolling back to a previous version or upgrading to a newer version is completed with comprehensible commands.
Resources and Conclusion.
- You can follow Kubesimplify.com an Initiative by Saiyam Pathak for encouraging beginners to get into the cloud world.
- You can follow Kunal Kushwaha in Twitter and also his amazing DevOps Boot Camp Youtube Channel
- Lens- The Kubernetes IDE

